
Satoko Ueno
Researcher (Isa-G)
- Position
- Program-Specific Researcher
- Research Field
- Neuroscience
- Personal Website
- https://nscinbiol.med.kyoto-u.ac.jp/en/member/satoko-ueno/
Research Overview
Gene regulatory networks associated with the massive re-routing of corticospinal tracts after spinal cord injury in non-human primates
The motor commands are conveyed by neural pathways from the brain to the muscles through the spinal cord. Therefore, when the spinal cord is injured, the motor functions are impaired because the motor commands are not delivered. It is known that the axons of these neural pathways are guided by interactions of multiple factors during neural development to reach the appropriate targets. Therefore, regeneration of the neural pathway to the same status as pre-injury condition is considered to be difficult in the developed adult brain.
Our previous studies focused on the trajectory of the corticospinal tract (CST) which is important for the dexterous hand movements in non-human primates. There, we observed the massive reorganization of CST in the monkeys which recovered their gross hand movements following the rehabilitative training and electrical stimulation of the brain after the large spinal cord injury. The trajectory of CST in this model was different from those of the intact monkeys, suggesting that the reorganized CST might have contributed to the recovered motor function.
Now, we hypothesize that the gene expression considerably changed in the neurons which showed the massive re-routing after the spinal cord injury. To elucidate the mechanism of the large-scaled reorganization of the neural pathway in the adult brain during the motor functional recovery from the spinal cord injury, we will analyze the gene regulatory network in the neurons that showed the reorganization after the spinal cord injury.
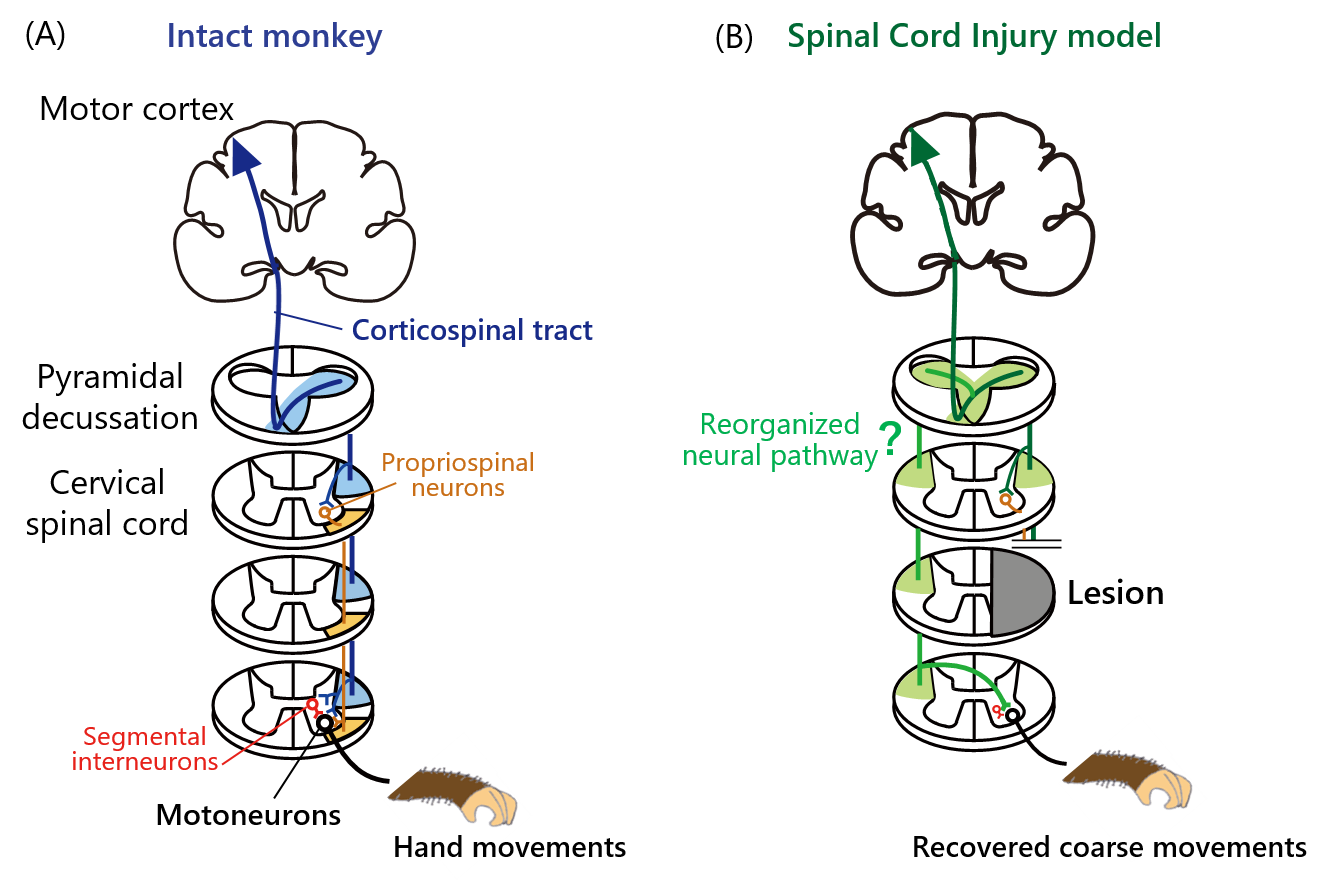
Figure 1: Neural pathway from the motor cortex to the spinal cord associated with hand movements in non-human primates. (A) In the intact monkey, the corticospinal tract (CST) descends and crosses to the contralateral side at the pyramidal decussation, and projects to the spinal cord. The motor command is delivered to the motoneurons which project to the muscles. (B) In the spinal cord injury models were observed the recovery of coarse hand movements, the CST projected differently from the intact monkey.
Biography
Publications
Satoko Ueno, Hiroshi Miyoshi, Yoko Maruyama, Mitsuhiro Morita, Shohei Maekawa, Interaction of dynamin I with NAP-22, a neuronal protein enriched in the presynaptic region,Neuroscience Letters,675,pp59-63,2018
Satoko Ueno, Keiji Seno, Yoko Maruyama, Fumio Hayashi, Hiroshi Miyoshi, Mitsuhiro Morita, Shohei Maekawa, Lipid Components in the Dynamin Fraction Prepared from Rat Brain,International Journal of Lipids,1,pp1-10,2018
Yoko Maruyama, Satoko Ueno, Mitsuhiro Morita, Fumio Hayashi, Shohei Maekawa, Inhibitory effect of several sphingolipid metabolites on calcineurin,Neuroscience Letters,673,pp132-135,2018
Joined
Apr. 16, 2022
