Research Overview
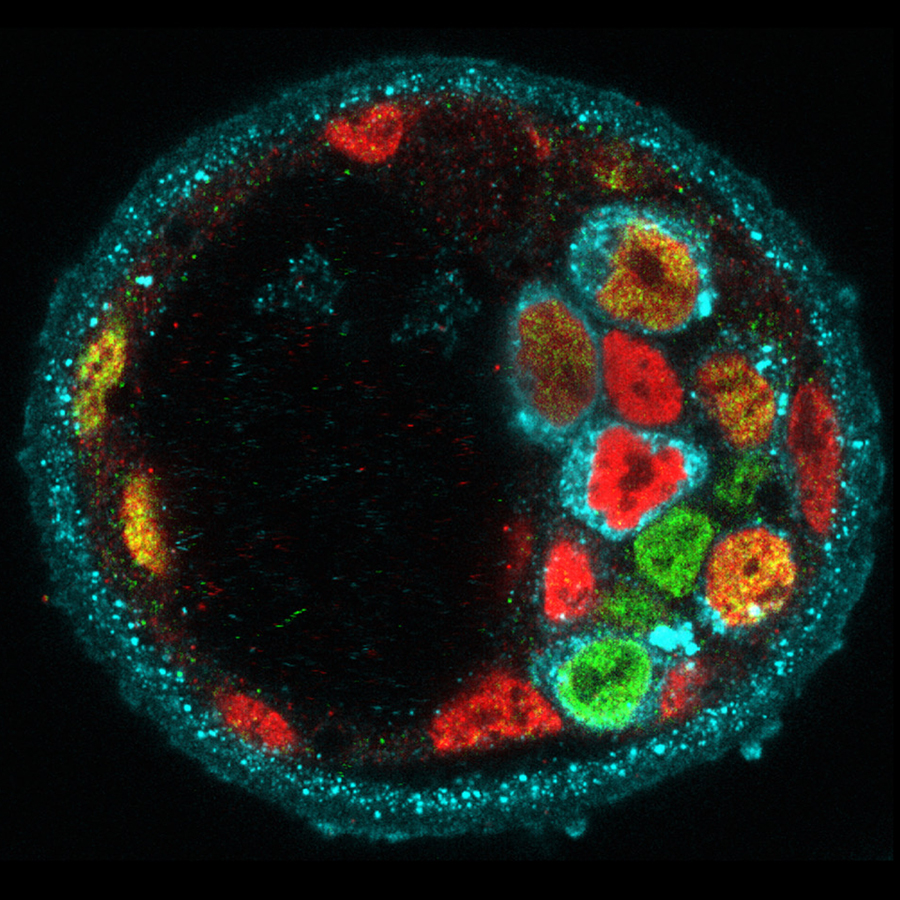
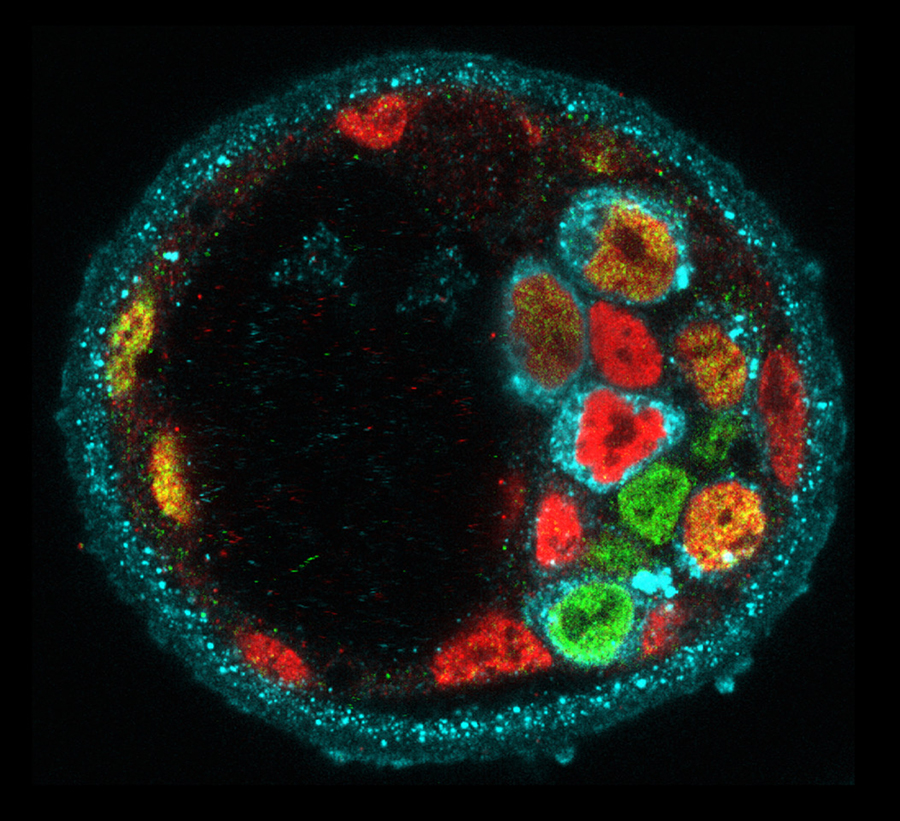
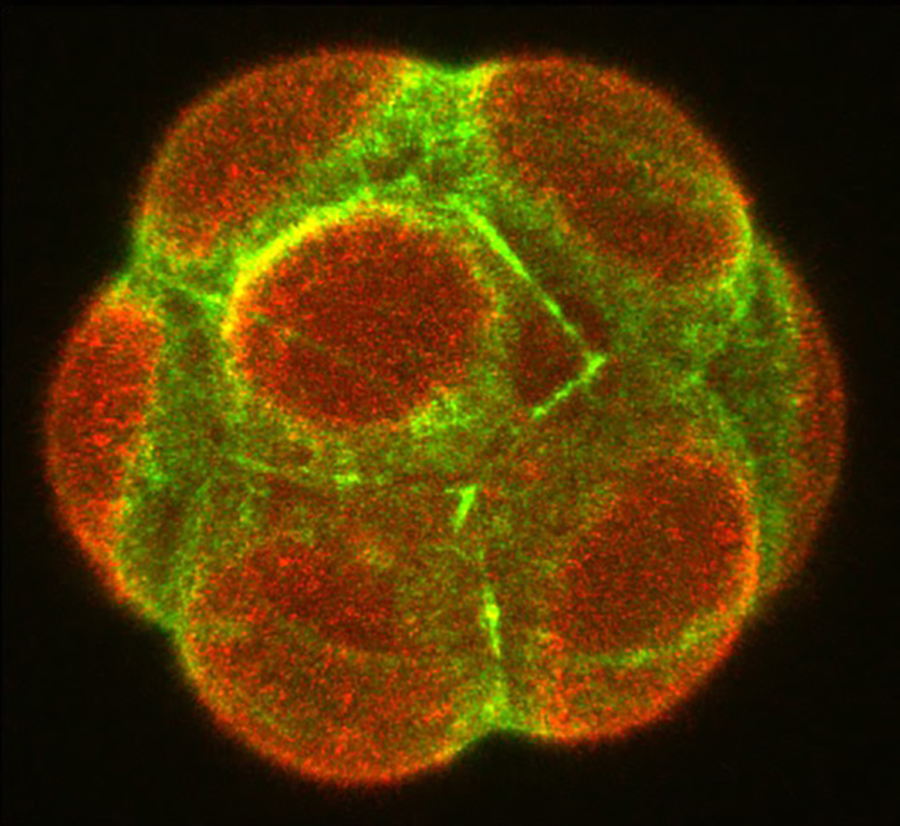
A defining feature of living systems is the capacity to break symmetry and generate well-defined forms and patterns through self-organisation. Our group aims to understand the design principle of multi-cellular self-organisation using early mammalian embryos. Our studies revealed that morphogenesis and gene expression in the early development are highly dynamic and stochastically variable in space and time (Figure 1). Determining how embryos robustly establish a size, shape and pattern at the right time despite the preceding variability remains a fundamental open question. We have recently developed an experimental framework that integrates biology, physics and mathematics (Figure 2). We aim to understand how molecular, cellular and physical signals are dynamically coupled across the scales for tissue self-organisation. Furthermore, we will identify developmental mechanisms shared and distinct among mammalian species. To this end, we will first establish the early primate developmental atlas at single-cell resolution by integrating single-cell omics data into 4D morphogenetic and lineage map derived from advanced microscopy. We adopt a wide variety of experimental strategies including embryology, genetics, advanced microscopy, biophysics and theoretical modelling in order to address fundamental questions in development and cell biology at molecular, cellular and systems levels.
Publications
Moghe, P., Belousov, R., Ichikawa, T., Iwatani, C., Tsukiyama, T., Erzberger, A., & Hiiragi, T. (2025). Coupling of cell shape, matrix and tissue dynamics ensures embryonic patterning robustness. Nature Cell Biology, 27(3). https://doi.org/10.1038/s41556-025-01618-9
Fabreges, D., Corominas-Murtra, B., Moghe, P., Kickuth, A., Ichikawa, T., Iwatani, C.,…Hiiragi, T. (2024). Temporal variability and cell mechanics control robustness in mammalian embryogenesis. Science, 386(6718), eadh1145. https://doi.org/10.1126/science.adh1145
Bondarenko, V., Nikolaev, M., Kromm, D., Belousov, R., Wolny, A., Blotenburg, M.,…Hiiragi, T. (2023). Embryo-uterine interaction coordinates mouse embryogenesis during implantation. Embo Journal, 42(17). https://doi.org/10.15252/embj.2022113280
Ichikawa, T., Zhang, H., Panavaite, L., Erzberger, A., Fabrèges, D., Snajder, R.,…Hiiragi, T. (2022). An ex vivo system to study cellular dynamics underlying mouse peri-implantation development [Article]. Developmental Cell, 57(3), 373-+. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.devcel.2021.12.023
Chan, C., Costanzo, M., Ruiz-Herrero, T., Mönke, G., Petrie, R., Bergert, M.,…Hiiragi, T. (2019). Hydraulic control of mammalian embryo size and cell fate. Nature, 571(7763), 112-+.
https://doi.org/10.1038/s41586-019-1309-x
Niwayama, R., Moghe, P., Liu, Y., Fabrèges, D., Buchholz, F., Piel, M., & Hiiragi, T. (2019). A Tug-of-War between Cell Shape and Polarity Controls Division Orientation to Ensure Robust Patterning in the Mouse Blastocyst Developmental Cell, 51(5), 564-+. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.devcel.2019.10.012
Ryan, A., Chan, C., Graner, F., & Hiiragi, T. (2019). Lumen Expansion Facilitates Epiblast-Primitive Endoderm Fate Specification during Mouse Blastocyst Formation Developmental Cell, 51(6), 684-+. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.devcel.2019.10.011
Korotkevich, E., Niwayama, R., Courtois, A., Friese, S., Berger, N., Buchholz, F., & Hiiragi, T. (2017). The Apical Domain Is Required and Sufficient for the First Lineage Segregation in the Mouse Embryo Developmental Cell, 40(3), 235-247. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.devcel.2017.01.006
Maître, J., Turlier, H., Illukkumbura, R., Eismann, B., Niwayama, R., Nédélec, F., & Hiiragi, T. (2016). Asymmetric division of contractile domains couples cell positioning and fate specification Nature, 536(7616), 344-+. https://doi.org/10.1038/nature18958