Research Overview
The germ-cell lineage ensures the creation of new individuals, perpetuating/diversifying the genetic and epigenetic information across the generations. We have been investigating the mechanism for germ-cell development, and have shown that mouse embryonic stem cells (mESCs)/induced pluripotent stem cells (miPSCs) are induced into primordial germ cell-like cells (mPGCLCs) with a robust capacity for both spermatogenesis and oogenesis and for contributing to offspring. These works have served as a basis for elucidating key mechanisms during germ-cell development such as epigenetic reprogramming, sex determination, meiotic entry, and nucleome programming.
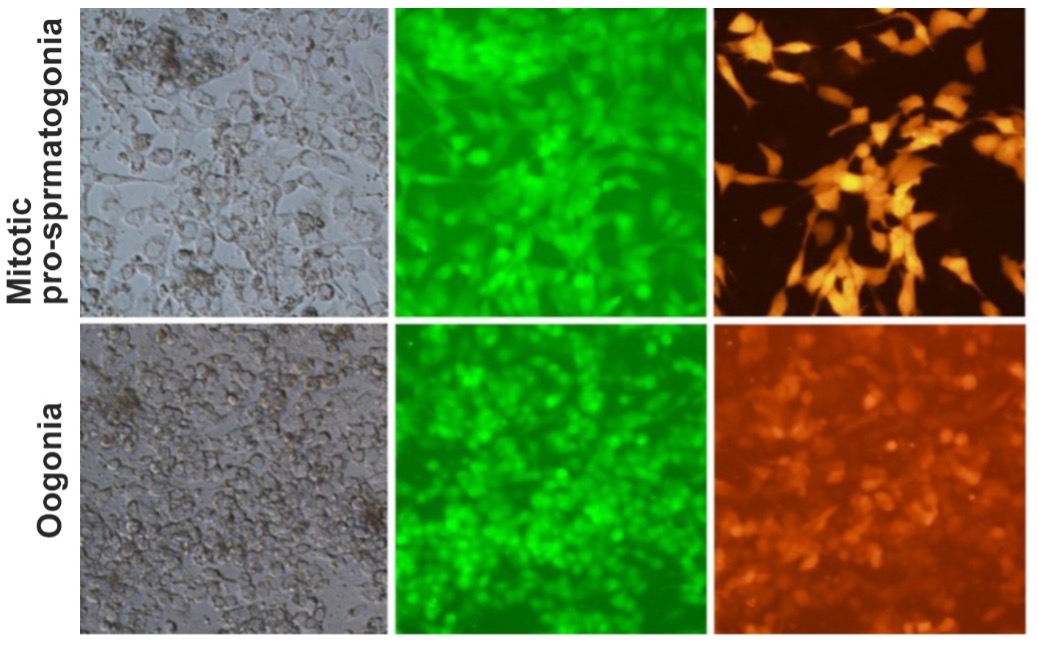
By investigating the development of cynomolgus monkeys as a primate model, we have defined a developmental coordinate of pluripotency among mice, monkeys, and humans, identified the origin of the primate germ-cell lineage in the amnion, and have elucidated the X-chromosome dosage compensation program in primates. Accordingly, we have succeeded in inducing human iPSCs (hiPSCs) into human PGCLCs (hPGCLCs) and elucidated the mechanism of human germ-cell specification, demonstrating that the mechanisms for germ-cell specification are evolutionarily divergent in many aspects between humans and mice. Furthermore, we have demonstrated an ex vivo reconstitution of fetal oocyte development in humans and monkeys, and an in vitro induction of meiotic fetal oocytes from ESCs in monkeys. More recently, we have established a robust strategy for inducing epigenetic reprogramming and differentiation of hPGCLCs into mitotic pro-spermatogonia or oogonia, coupled with their extensive amplification (~>1010-fold). These studies have established a foundation for human in vitro gametogenesis. We are aiming to advance it further to delineate the mechanism of human germ-cell development and to create a basis for new possibilities in reproductive medicine.
Publications
Murase, Y., Yokogawa, R., Yabuta, Y., Nagano, M., Katou, Y., Mizuyama, M., Kitamura, A., Puangsricharoen, P., Yamashiro, C., Hu, B., Mizuta, K., Ogata, K., Ishihama, Y., & Saitou, M. (2024). In vitro reconstitution of epigenetic reprogramming in the human germ line. Nature. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41586-024-07526-6
Mizuta, K., & Saitou, M. (2023). Key mechanisms and in vitro reconstitution of fetal oocyte development in mammals. Current Opinion in Genetics & Development, 82, 102091. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.gde.2023.102091
Gyobu-Motani, S., Yabuta, Y., Mizuta, K., Katou, Y., Okamoto, I., Kawasaki, M., Kitamura, A., Tsukiyama, T., Iwatani, C., Tsuchiya, H., Tsujimura, T., Yamamoto, T., Nakamura, T., & Saitou, M. (2023). Induction of fetal meiotic oocytes from embryonic stem cells in cynomolgus monkeys. EMBO Journal, 42(9), e112962. https://doi.org/10.15252/embj.2022112962
Imoto, Y., Nakamura, T., Escolar, G. E., Yoshiwaki, M., Kojima, Y., Yabuta, Y., Katou, Y., Yamamoto, T., Hiraoka, Y., & Saitou, M. (2022). Resolution of the curse of dimensionality in single-cell RNA sequencing data analysis. Life Science Alliance, 5(12), e202201591. https://doi.org/10.26508/lsa.202201591
Mizuta, K., Katou, Y., Nakakita, B., Kishine, A., Nosaka, Y., Saito, S., Iwatani, C., Tsuchiya, H., Kawamoto, I., Nakaya, M., Tsukiyama, T., Nagano, M., Kojima, Y., Nakamura, T., Yabuta, Y., Horie, A., Mandai, M., Ohta, H., & Saitou, M. (2022). Ex vivo reconstitution of fetal oocyte development in humans and cynomolgus monkeys. EMBO Journal, 41(18), e110815. https://doi.org/10.15252/embj.2022110815
Ishikura Y, Ohta H, Nagano M, Saitou M. Optimized protocol to derive germline stem-cell-like cells from mouse pluripotent stem cells. (2022) STAR Protoc., 3(3):101544. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.xpro.2022.101544
Nagano, M., Hu, B., Yokobayashi, S., Yamamura, A., Umemura, F., Coradin, M., Ohta, H., Yabuta, Y., Ishikura, Y., Okamoto, I., Ikeda, H., Kawahira, N., Nosaka, Y., Shimizu, S., Kojima, Y., Mizuta, K., Kasahara, T., Imoto, Y., Meehan, K., Stocsits, R., Wutz, G., Hiraoka, Y., Murakawa, Y., Yamamoto, T., Tachibana, K., Peters, J. M., Mirny, L. A., Garcia, B. A., Majewski, J., & Saitou, M. (2022). Nucleome programming is required for the foundation of totipotency in mammalian germline development. EMBO Journal, 41(13), e110600. https://doi.org/10.15252/embj.2022110600